Summary
In children with moderate to severe persistent asthma, macrolide (Mac) or leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA) will provide the same steriod-sparing effect when compared to placebo as the dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) is reduced. This will be tested following achievement of control symptoms with moderate to high dose ICS in combination with long-acting bronchodilator agonist (LABA). Use of these ICS doses will be based on NHLBI step-up guideline to achieve asthma control.
Design
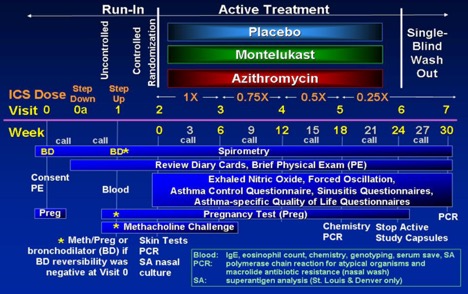
MARS is designed as a randomized, double-blind parallel-group that compares the capacity of azithromycin or montelukast to placebo as effective therapy that allows ICS reduction in children 6 to 17 years with moderate to severe persistent asthma.
Population
Childhood Asthma Research and Education (CARE) Network
Enrollment for MARS began in February 2006 with a target sample size of 210 randomized children (70 on placebo, 70 on montelukast, and 70 on azithromycin). The CARE Network DSMB, however, recommended to the NHLBI that the MARS trial be terminated due to the results of a futility analysis based on 55 randomized children. The NHLBI accepted this recommendation, so the trial was terminated on March 07, 2007. No differences were noted for either treatment compared to placebo in time to inadequate control status (median, weeks (95% CL) azithromycin: 8.4 (4.3, 17.3), montelukast 13.9 (4.7, 20.6), placebo 19.1 (11.7, infinity)), with no difference between the groups (log rank test, p = 0.49). The major manuscript is in press at JACI.
Strunk RC, Bacharier LB, Phillips BR, Szefler SJ, Zeiger RS, Chinchilli VM, Martinez FD, Lemanske Jr RF, Taussig LM, Mauger DT, Morgan WJ, Sorkness CA, Paul IM, Guilbert T, Krawiec M, Covar R, Larsen G. Azithromycin or montelukast as inhaled corticosteroid-sparing agents in moderate to severe childhood asthma study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2008; 122:6:1138-1144.e4. PMID: 18973936.

